Table of Contents
Evaporation of water in an aquarium is a process where water changes from liquid to gas, releasing moisture into the environment. It is a natural phenomenon resulting from the temperature difference between the water and the air, as well as the movement of air over the water surface. Evaporation is a common issue in maintaining marine aquariums. The rate of water evaporation can vary greatly depending on factors such as air temperature, humidity, evaporation surface area, and whether the aquarium is covered or not.
Causes and factors influencing evaporation
Temperature and humidity
The rate of water evaporation in an aquarium is strongly linked to the water temperature and the surrounding environment. A larger temperature difference between the aquarium water and the environment favors an increased evaporation rate as warm water gives off heat to the cooler air. Conversely, when the water temperature is lower than the room temperature, the evaporation rate decreases, since warmer water tends to evaporate faster, especially when the surrounding air is cooler and can absorb more water vapor. If the surrounding air temperature is significantly higher than the water temperature in the aquarium, it still promotes the evaporation process.
Air humidity
Air humidity also plays a crucial role in the amount of water evaporated in the form of water vapor. In winter, when indoor air is often dry due to heating, the air can absorb more moisture, thereby increasing evaporation. However, in the case of high humidity, when the air is already saturated with water vapor, the rate of evaporation decreases.
Surface area and water movement
Tanks with a larger water surface area are exposed to air, thus naturally experiencing a higher rate of evaporation. Additionally, increased water movement caused by pumps or circulators can increase evaporation.
Using fans to cool the water, especially in summer, can significantly increase the amount of evaporated water, as air movement speeds up the evaporation process. It’s worth mentioning here that warmer water has a lower surface tension, which facilitates the evaporation of water molecules.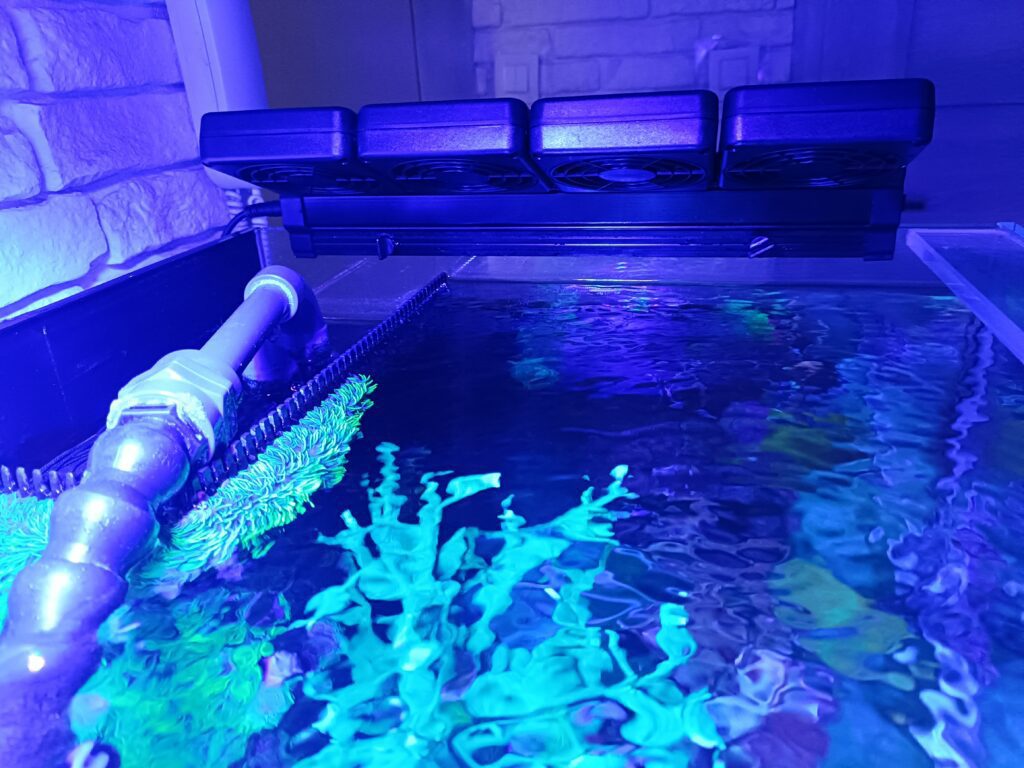
Tank configuration
Open aquariums, i.e., those that are not covered with lids or other coverings, tend to evaporate water faster due to direct contact with the surrounding air. However, tanks with covers or coverings can significantly reduce evaporation by limiting water exposure to the air, although this can be associated with some issues such as increased temperature.
Managing evaporation
To effectively manage evaporation in a marine aquarium, consider the following strategies.
Use of covers or lids
Installing a glass or acrylic cover can help reduce evaporation by minimizing water surface exposure to the air. However, covering the tank can also lead to some undesirable effects:
- Limiting heat exchange: When the tank is covered, heat exchange with the environment mainly occurs through the covering material, which may be a poor conductor of heat. As a result, if a lamp hanging over the tank also generates heat, dissipating this energy can be problematic and consequently may lead to an increase in tank temperature.
- Reducing access to UV radiation: Materials such as glass can limit access to UV radiation, which is crucial for some marine organisms, such as symbiotic algae.
- Cooling issues: In the situation of increased temperature in a tank with a cover or lid, mounting fans that help lower the temperature becomes less effective in a closed aquarium due to restricted air exchange limiting heat dissipation.
Maintaining room conditions
Maintaining a stable temperature and humidity in the room where the aquarium is located can help minimize fluctuations in the evaporation rate. Avoid placing the tank near heat sources or in direct sunlight to prevent excessive water loss.
Automatic Water Top-Off Systems (ATO)
For convenience and maintaining stable water conditions, particularly salinity, an automatic water top-off system is the optimal solution. These systems automatically replenish water that has evaporated, maintaining a constant water level in the aquarium. A device such as the Level Keeper Reef Factory is an advanced automatic water top-off system that ensures water condition stability in the aquarium and minimizes the need for manual intervention. The device has two sensors that monitor the water level, and the water top-off pump activates only when both detect a too low level.
Conclusion
Evaporation in marine aquariums is a natural process that significantly affects water salinity, which is particularly important in open aquariums where direct contact with air accelerates this process. Managing evaporation is crucial for maintaining stable water conditions, essential for the health of marine organisms. To effectively control evaporation and its impact on salinity, it is recommended to use automatic water top-off systems. These systems, by monitoring the water level and automatically replenishing it, prevent sudden changes in salinity, which are critical for marine organisms, especially corals.
About the author

Grzegorz Bubak
My fascination with marine aquariums began over two decades ago when I stumbled upon an article about this topic in a magazine. Since then, the underwater world has become my obsession and passion, shaping my everyday life. I started my adventure with marine aquariums with soft corals, which were my first step into this fascinating world. Over time, captivated by the diversity and beauty of SPS corals, I decided to focus on their cultivation, which continues to fill me with constant wonder.
Thanks to my experience and passion for marine aquariums, I am ready to share my knowledge and expertise with other enthusiasts in this field. I am happy to be part of the Reef Pedia community, which serves as an invaluable source of information for all marine aquarium lovers.