Table of Contents
What exactly is ZOOPLANKTON?
By scientific definition, zooplankton consists of small animal organisms. It’s a highly diverse group, including representatives from various invertebrate groups, such as rotifers, copepods, and appendicularia.
In aquarium terms, zooplankton is suspended microorganisms in the water, serving as natural food for corals or fish.
The importance of zooplankton in a marine aquarium
In maintaining a marine aquarium, it’s important to be aware that zooplankton is an integral part of the food chain* and plays a role just as crucial as phytoplankton. You’ve probably heard about the food chain in one of your biology classes. Assuming not everyone remembers what it entails, let me explain the concept now.
The food chain describes the nutritional relationships among various organisms in an ecosystem. In the simplified diagram below, you can see the basic flow of energy and matter.
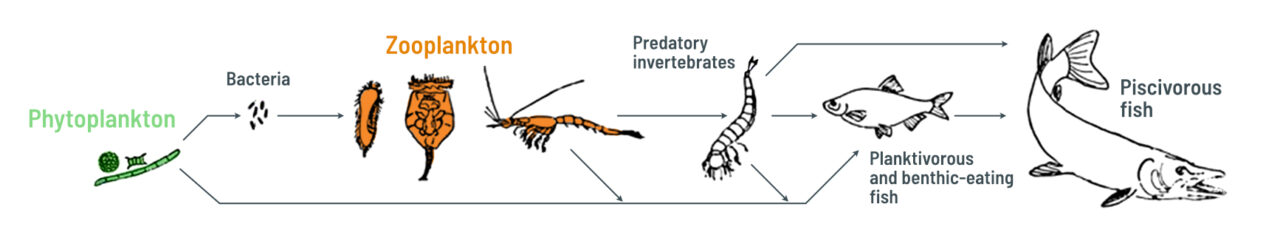
In simple terms, the food chain describes the transfer of energy and matter from producers, which are organisms that undergo photosynthesis (like phytoplankton), to consumers, which are organisms that feed on other organisms (like zooplankton or fish). In short, the food chain illustrates the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another.
Most aquarium keepers use zooplankton because of its beneficial impact on aquarium ecosystems. Zooplankton serves as a valuable diet for other organisms, such as corals and fish.
The role of zooplankton in marine aquariums
Nutritional role
Zooplankton primarily serves as a crucial food source for a wide range of organisms in marine aquariums, including corals, fish, invertebrates, and others. It provides them with essential nutrients such as proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals, necessary for growth, development, and overall health. By ensuring an adequate quantity and quality of zooplankton in the marine aquarium, we supply marine animals with a variety of nutrients.
Regulatory role
Zooplankton regulates the population of phytoplankton, feeding on them to maintain balance in marine tanks. Controlling the growth of phytoplankton is crucial for water clarity and the overall ecosystem quality of the aquarium. Zooplankton not only feeds on phytoplankton but also on bacterioplankton.
Additionally, zooplankton can remove organic particles by consuming detritus, which is dead organic matter floating in the water. By consuming detritus, zooplankton contributes to its decomposition and mineralization, helping to maintain water cleanliness and prevent excessive accumulation of organic substances.
Role – coral coloration
Zooplankton contains many valuable components that positively impact the coloration of corals. Examples include carotenoids (such as beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, lutein), which influence the color of corals. By providing an adequate amount of zooplankton, you can help maintain the beautiful, natural colors of these organisms.
Zooplankton composition
The qualitative and quantitative composition of zooplankton depends on various factors, such as the availability of nutrients (food), water temperature, oxygen concentration in the water, and the pressure from predators.
Zooplankton species serve as integral components of aquatic food chains, acting as consumers in these ecosystems. Considering their heterotrophic feeding mode, zooplankton relies on phytoplankton and other autotrophic organisms as primary sources of energy and carbon compounds.
Zooplankton consists of a wide variety of microorganisms with a broad spectrum of sizes, ranging from tiny protozoa to considerably larger organisms. Sometimes, young forms of certain animals, such as larvae, may transiently join the ranks of zooplankton.
The common feature of zooplankton (small animal organisms) is that they act as a link in food chains, transferring energy from producers (phytoplankton) to higher trophic levels, influencing the nutrient cycle in aquatic environments. The most well-known representatives of zooplankton are:
- Copepods: they are one of the most numerous species of zooplankton. They are small crustaceans with a tear-shaped body and long antennae
- Rotifers: microscopic, multicellular animals
- Flagellates
- Polychaetes
It’s important to remember that using zooplankton of unknown origin can lead to water contamination or, in extreme cases, the infection of animals. When using commercially available products, choose only those of high quality and purity.
Unlike other chemical preparations or supplements, zooplankton, like phytoplankton, must be stored correctly because it is a living product! Proper storage of zooplankton as a living product is essential for its effectiveness and nutritional value. If it is not stored under suitable conditions, it may degrade, die, or lose its properties.
Problems related to the deficiency or excess of zooplankton in seawater
Zooplankton is one of the best natural foods used in marine aquariums. Nevertheless, its role in a marine aquarium is significant. Firstly, zooplankton feeds on phytoplankton, bacterioplankton, and detritus, helping maintain a balance of nutrients and decompose organic matter. Therefore, regularly providing zooplankton in the marine aquarium supports coral nutrition, growth, and proper development.
In aquarium conditions, zooplankton is often captured by pumps and protein skimmers. There is often a shortage of it. However, with a tendency to frequently feed animals with zooplankton, there are cases of an excess of zooplankton in the tank.
How to protect your aquarium?
It’s crucial to maintain it at the right level to preserve the ecosystem balance and ensure the health of all organisms. Using high-quality zooplankton from a reliable source and storing it properly is essential. Regularly cleaning filters, providing proper lighting, controlled feeding, and using suitable additives help prevent an excess of zooplankton.
Recommendations
To make sure you have the right level of zooplankton in your aquarium, you should dose it according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and maintain the proper level. If the recommended zooplankton level is exceeded, reduce the parameter value in the water. Perform up to 6 water changes, replacing about 15% of the aquarium water each time until you reach the recommended parameter value. The replacement water must have the correct target salinity. Use salt with appropriate parameters and composition for ICP testing.
If the zooplankton level is low, it’s recommended to use zooplankton from a supplier declaring high-quality and purity to balance its level. To maintain a steady zooplankton level in a marine aquarium, we recommend regularly supplementing this component based on the coral population in your tank.
Summary
In summary, zooplankton is a crucial component of marine aquarium ecosystems. Its role as a link in the food chain, a food source for fish and corals, and a participant in the nutrient cycle makes it incredibly important for the healthy and balanced functioning of aquariums. Therefore, it’s worthwhile to include zooplankton in the diet of marine animals.
* Wilk-Woźniak E. 2016. Fitoplankton. W : Sądag T., Banduła T., Materek E., Mazurkiewicz-Boroń G. & Słonka R. (red.) Zbiornik wodny Dobrzyce-monografia, Kraków: RZGW, MPWiK: 158-166.
About author

Magdalena Metzler
Privately, I am a mother and a lover of nature and sport. My main interest is quantum chemistry, which hides a whole lot of unsolved mysteries and connections, which is extremely exciting from a scientific point of view.
In my scientific career, I have conducted international projects focused on innovative solutions for many branches of business, e.g. automotive, construction, and now, of course, marine aquaristics.
Working at Reef Factory gave me a passion for marine aquaristics, which I can develop every day, building a chemistry department and creating products that will help aquarists take care of tanks and ensure the highest safety of animals. One of the most exciting memories of working at Reef Factory is the commissioning of the ICP-OES spectrometer, which analyzes the elemental composition of seawater. The method of analysis in ICP is based on an analytical technique, which is a combination of my passion for quantum chemistry and marine aquaristics.
I hope you find my articles on ReefPedia interesting and helpful! Happy reading :))

